The 9 Dangerous Impact of Alcohol on Health and Fitness

Introduction
Alcohol consumption has been deeply ingrained in many cultures for centuries, playing a significant role in social gatherings, celebrations, and even religious ceremonies. While moderate alcohol consumption may have some potential health benefits, excessive or chronic use can have detrimental effects on both physical health and fitness goals. In this article, we’ll explore the impact of alcohol on various aspects of health and fitness, shedding light on its potential consequences.
(https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=_-skVpmoaGI&t=18s)
Understanding Alcohol Consumption:
Alcohol, chemically known as ethanol, is a psychoactive substance that affects the central nervous system. It is commonly found in beverages such as beer, wine, and spirits. The effects of alcohol consumption vary depending on factors such as the amount consumed, the individual’s tolerance, and their overall health.
Health Implications:
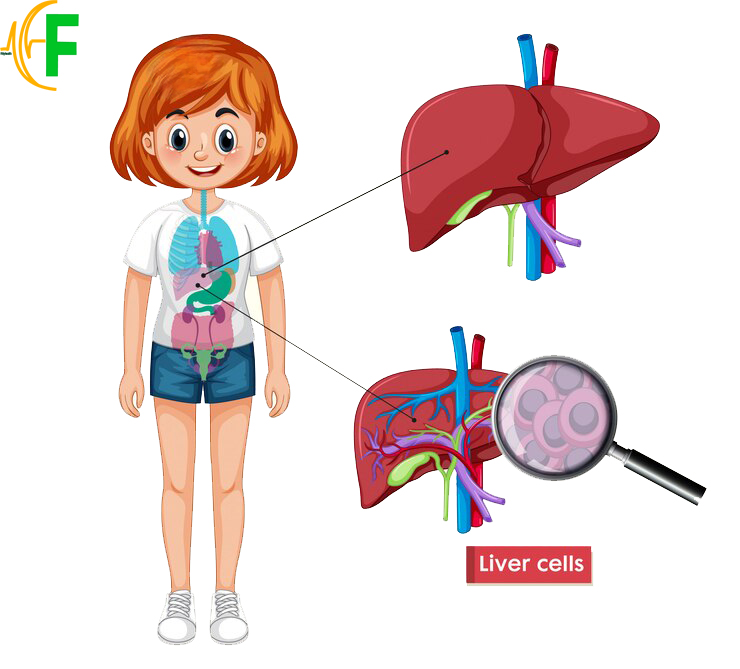
1. Liver Health:
One of the most well-known consequences of excessive alcohol consumption is liver damage. The liver plays a crucial role in metabolizing alcohol, but excessive intake can lead to inflammation, fatty liver disease, hepatitis, and ultimately, cirrhosis. Chronic alcohol abuse significantly increases the risk of developing these conditions, which can ultimately lead to liver failure and the need for a liver transplant.
- The liver plays crucial roles in the body, including removing toxins .
- It processes nutrients from food and helps regulate metabolism .
- To maintain liver health, avoid touching or inhaling toxins found in cleaning products, aerosols, and insecticides .
- Carefulness with herbs is advised, as some may have adverse effects on liver health .
- A healthy diet rich in foods like vegetables, fruits, whole grains, and lean proteins supports liver health .
- Limit alcohol consumption, as excessive drinking can lead to liver damage.
2. Cardiovascular Health:
While moderate alcohol consumption has been associated with a reduced risk of cardiovascular disease, excessive drinking can have the opposite effect. Heavy drinking can lead to high blood pressure, irregular heart rhythms, cardiomyopathy (weakening of the heart muscle), and an increased risk of stroke. These cardiovascular complications can significantly impact overall health and increase mortality rates.
- Symptoms of CVDs vary but may include chest pain, shortness of breath, fatigue, and irregular heartbeat.
- Prevention strategies for heart disease include adopting a heart-healthy lifestyle, such as maintaining a balanced diet, regular exercise, managing stress, and avoiding smoking .
- The American Heart Association recommends focusing on “Life’s Simple 7” factors for cardiovascular health: manage blood pressure, control cholesterol, reduce blood sugar, get active, eat better, lose weight, and stop smoking.
3. Mental Health:
Alcohol is a depressant that can affect mood and cognitive function. While some individuals may use alcohol as a coping mechanism for stress or anxiety, excessive consumption can exacerbate mental health issues and increase the risk of developing conditions such as depression and anxiety disorders. Long-term alcohol abuse is also associated with an increased risk of dementia and cognitive decline.
- Mental health encompasses emotional, psychological, and social well-being.
- It influences how individuals think, feel, and behave, and impacts their ability to cope with stress, relate to others, and make decisions .
- Mental illnesses are prevalent worldwide, with conditions such as depression, anxiety disorders, and schizophrenia affecting millions of people.
- Stigma remains a significant barrier to seeking help for mental health issues, often leading to discrimination and social isolation.
- Mental, neurological, and substance use disorders collectively contribute to a significant portion of the global burden of disease, highlighting the importance of addressing mental health on a global scale.
4. Cancer Risk:
Alcohol consumption has been linked to an increased risk of various types of cancer, including liver, breast, colorectal, and esophageal cancer. The exact mechanisms behind this association are not fully understood, but it is believed that alcohol can damage DNA, impair the immune system, and increase inflammation, all of which can contribute to the development of cancer.
- Cancer risk refers to the likelihood that an individual will develop cancer during their lifetime.
- Modifiable risk factors such as smoking, alcohol consumption, poor diet, and physical inactivity contribute to more than 40% of cancer-related deaths .
- Lifestyle factors play a significant role in cancer risk, with most cancers attributed to environmental and behavioral factors rather than hereditary origins.
- Specific environmental factors, like smoking for lung cancer and excessive sunlight exposure for skin cancer, are known contributors to cancer risk .
- Radiation exposure is another significant factor affecting cancer risk, with various sources of radiation posing different levels of risk .
- Data from studies on atomic bomb survivors and other populations help estimate cancer risks associated with radiation exposure and other environmental factors.
5. Immune Function:
Excessive alcohol consumption can weaken the immune system, making individuals more susceptible to infections and illnesses. Chronic alcohol abuse can impair the body’s ability to produce immune cells and antibodies, leaving it vulnerable to pathogens. This can lead to an increased risk of infections such as pneumonia and tuberculosis.
- The immune system is a complex network of organs, cells, and proteins that defend the body against infections and diseases.
- It protects the body from harmful substances, germs, and abnormal cell changes that could lead to illness .
- Immune responses involve various lines of defense against microbes, including physical barriers, innate immune responses, and adaptive immune responses .
- Different types of immune cells, such as T cells, B cells, macrophages, and natural killer cells, play specific roles in recognizing and eliminating pathogens .
- The immune system’s function can be influenced by factors such as genetics, age, diet, stress, and environmental exposures.
1. Nutritional Implications:
Alcohol is high in empty calories and provides little to no nutritional value. Consuming alcohol in excess can contribute to weight gain and hinder progress towards fitness goals such as weight loss or muscle gain. Additionally, alcohol consumption can disrupt nutrient absorption and metabolism, leading to deficiencies in essential vitamins and minerals.
- Nutrition plays a crucial role in maintaining overall health and well-being by providing essential nutrients that support various bodily functions.
- A balanced diet that includes a variety of nutrient-dense foods is important throughout life stages to meet changing nutritional requirements .
- Nutritional implications refer to the effects of dietary choices on health outcomes, including the risk of developing chronic diseases such as obesity, diabetes, cardiovascular diseases, and certain cancers.
- Understanding nutrition helps individuals make informed choices about their diet to support optimal health and prevent nutritional deficiencies.
- Nutritional labels on food products provide information about key nutrients, helping consumers make healthier choices and meet their dietary needs.
- Balanced nutrition involves consuming a variety of macronutrients (carbohydrates, proteins, and fats) and micronutrients (vitamins and minerals) in appropriate amounts to support metabolic functions and maintain health .
2. Impaired Muscle Recovery:
Alcohol consumption can interfere with muscle recovery processes following exercise. It can increase inflammation, disrupt protein synthesis, and impair the body’s ability to repair and rebuild muscle tissue. This can prolong recovery times and negatively impact athletic performance over time.
- Impaired muscle recovery refers to the inability of muscles to properly recover and repair after exercise-induced damage.
- Factors such as age, gender, fitness level, and underlying health conditions can influence the extent of muscle damage and subsequent recovery.
- Inflammation is a natural response to muscle damage but excessive or prolonged inflammation can hinder the recovery process.
- Hydration status plays a crucial role in muscle recovery, with dehydration (>2% reduction in body mass) impairing both exercise performance and recovery.
- Sleep is essential for effective muscle recovery, as it allows the body to repair damaged tissues and replenish energy stores.
- Proper nutrition, including adequate intake of protein, carbohydrates, and micronutrients, supports muscle recovery by providing essential building blocks and nutrients.
3. Disrupted Sleep Patterns:
While alcohol may initially act as a sedative and help individuals fall asleep faster, it can disrupt sleep patterns and impair the quality of restorative sleep. Poor sleep quality can affect energy levels, mood, and cognitive function, ultimately hindering athletic performance and recovery.
- Disrupted sleep patterns refer to irregularities or disturbances in the normal sleep cycle, including difficulties falling asleep, frequent awakenings during the night, or waking up too early.
- Causes of disrupted sleep patterns can include stress, anxiety, medical conditions like sleep disorders, environmental factors such as noise or light, lifestyle habits like irregular sleep schedules, and certain medications.
- Consequences of disrupted sleep patterns include daytime sleepiness, fatigue, impaired cognitive function, mood disturbances, decreased productivity, and an increased risk of accidents.
- Disrupted sleep can negatively impact various aspects of life, including relationships, work performance, and overall well-being.
- Addressing underlying causes and implementing good sleep hygiene practices, such as maintaining a regular sleep schedule, creating a comfortable sleep environment, and managing stress, can help improve disrupted sleep patterns.
4. Increased Injury Risk:
Alcohol impairs judgment, coordination, and reaction time, increasing the risk of accidents and injuries during physical activity. Whether engaging in sports, weightlifting, or other forms of exercise, impaired motor skills can lead to falls, strains, and other injuries that can derail fitness progress and sideline individuals from their training routine.
- Increased injury risk refers to a higher likelihood of experiencing injuries during physical activity or sports participation.
- Factors contributing to increased injury risk include over-training, incorrect sports technique, inadequate nutrition, and poor training practices.
- Specific risk factors such as strength, balance, joint mobility, and movement patterns may also play a role in predicting injuries.
- Injury prevention strategies include proper training techniques, adequate rest and recovery, maintaining a balanced diet, and addressing any underlying risk factors through targeted exercises or interventions.

Conclusion:
While moderate alcohol consumption may have some potential health benefits, excessive or chronic use can have serious implications for both physical health and fitness goals. From liver damage and cardiovascular complications to impaired muscle recovery and increased injury risk, the negative effects of alcohol on health and fitness are wide-ranging. Individuals looking to optimize their health and achieve their fitness goals should be mindful of their alcohol intake and strive to maintain a balanced and moderate approach to consumption. By prioritizing moderation and making informed choices, individuals can minimize the negative impact of alcohol on their health and fitness journey.